Faster Finality
How transactions achieve finality in Quai Network.
What is Finality?
When you send a transaction, how long do you have to wait before you’re confident it can’t be reversed? This waiting time is called finality.Two Types of Finality:
Statistical Finality: Mathematical certainty your transaction is permanent (barring a 51% attack)
Economic Finality: The cost to reverse your transaction exceeds any attacker’s benefit
Why Faster Finality Matters:
Better user experience: No waiting 10+ minutes for Bitcoin confirmations
Enables commerce: Merchants can accept payments instantly
Reduces uncertainty: Clear when transactions are truly final
The Challenge: Quai’s Multi-Chain Architecture
Quai Network uses a hierarchy of blockchains:
Prime chains: Main coordination chains (slower, more secure)
Region chains: Regional coordination chains
Zone chains: Individual transaction chains (faster, where users interact)
The Problem: In traditional systems, transactions on fast chains (zones) aren’t final until confirmed by slow chains (prime). This creates uncertainty.
The Withholding Attack Problem
What’s a Withholding Attack? Imagine a miner finds a valid block but doesn’t immediately broadcast it. Instead, they hold it back while other miners waste energy mining the previous block.In Single Chains (like Bitcoin):
Attacker holds back a block for ~10 minutes
Minimal impact since no transactions process between blocks
Eventually another miner finds a block, making the withheld block worthless
In Multi-Chain Systems (Traditional Approach):
Zone chains process transactions continuously
But those transactions aren’t final until prime chain confirms
Attacker could hold back a prime block, keeping zone transactions uncertain
Much more disruptive than single-chain attacks
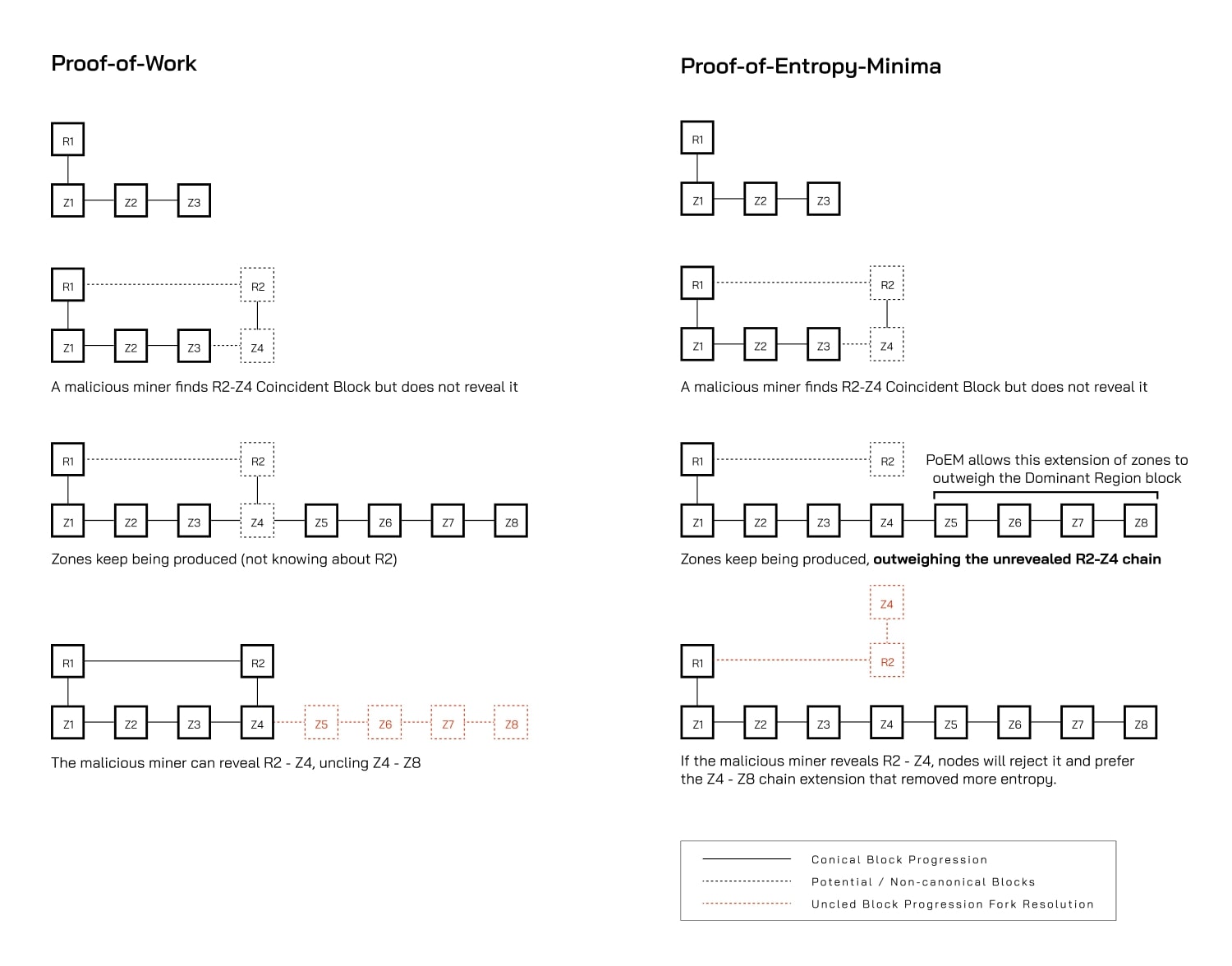
PoEM’s Solution: Bottom-Up Finality
Traditional Hierarchy (Top-Down):
Prime chains lead, zone chains follow
Zone transactions wait for prime confirmation
Vulnerable to prime chain withholding attacks
PoEM Hierarchy (Bottom-Up):
Zone chains can achieve finality independently
Prime chains follow zone chain entropy accumulation
Withholding attacks become ineffective
How This Works:
Zone chains remove entropy faster than prime chains (due to higher frequency)
Even the “luckiest” possible prime block can’t outweigh zone chain accumulation for long
Transactions achieve finality in seconds, not minutes
Finality Comparison
Bitcoin
10+ minutes (1 block)
Wait for longest chain
Ethereum
12+ minutes (2 epochs)
Wait for 2/3 validator approval
Quai PoEM
~5 seconds (1 zone block)
Entropy accumulation measurement
Why PoEM is Faster:
Objective measurement: Entropy is mathematically scarce, not subjective
Independent chains: Zone finality doesn’t depend on prime blocks
Precise calculation: Measures exact work, not arbitrary thresholds
Learn more about the mathematical details of this calculation.
Economic Finality: Real-World Security
What is Economic Finality? The point where reversing your transaction would cost an attacker more than they could possibly gain.Real-World Examples:
Coffee purchase ($5): Economically final almost instantly
Car purchase ($50,000): May need 30+ minutes for full economic security
House purchase ($500,000): Could require hours of confirmations
Factors Affecting Economic Finality:
Transaction value: Higher value = longer wait time needed
Network hashrate: More miners = better security = faster finality
Pending transactions: Network congestion affects attack costs
Market conditions: Token price volatility impacts attack economics
Built-in Economic Finality Tool
Quai Network includes a smart finality calculator that:Analyzes Network Conditions:
Current hashrate and mining distribution
Pending transaction volumes and fees
Historical attack costs and patterns
Provides Custom Recommendations:
Instant decisions for small transactions
Precise wait times for large transfers
Real-time updates as conditions change
Use Cases:
Merchants: Know exactly when payments are safe
Exchanges: Minimize deposit wait times while maintaining security
Users: Understand the security level of their transactions
Last updated